Telangiectatic rosacea is a widespread condition, especially among northern European populations, who generally have fair skin and blue eyes. It is characterised by rash (or erythrosis) with small vessels, telangiectasias or couperose with larger vessels and facial flushing in some cases. The whole face can be affected (except for the periocular and peribuccal regions).
Patients’ demand for an effective treatment against such a visible condition is important. It is commonly treated using laser or pulsed-light systems.
The Nd:YAG laser emits a 1064 nm wavelength beam, which is poorly absorbed by melanin, and therefore penetrates deeply into the skin. Using long pulse lengths, this laser is specifically effective on large telangiectasias, such as those located on the nose. Its multi-pulsed emission mode allows for the use of less power, protecting the surrounding tissues. Furthermore, its mode of action induces a photo-coagulation mechanism of action, preventing post-treatment the formation of purpura.
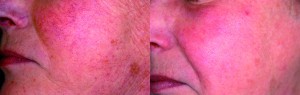
Figure 1 Phototype III, 65-year-old woman with mixed couperose characterised by large telangiectasia on the cheekbones and nose, and thinner vessels on the other parts of the face. (left) Heliodermia with pigmentary spots is also present. The Nd:YAG laser was used during the first session with 85 J, 15 ms and 2.5 mm handpiece to remove the larger vessels. Three further sessions followed with a 1-month gap between, using the FT pulsed light system. A single application was carried out on the face and neck base with a 500 nm filter, 15 J, 8 ms (right). The aim was to remove the thinnest vessels and pigmentation
Pulsed light impacts on different vessels according to the pulse width. For medium vessels, less than 10 ms is preferred to prevent purpura formation after treatment. The 500 nm vessel filter is the most effective for this condition, provided it is used on fair skins.
Treating marked telangiectatic rosacea requires between three and five treatment sessions spaced 1 month apart. During the first session, the Nd:YAG laser is specifically recommended for dark (purple) telangiectasias. Therefore, during the first session greater vessels (which are usually found on the nose, chin, cheek, etc.) are treated.
Pulsed light is used during subsequent sessions, as it is more effective on thinner vessels. During pulsed light sessions, the Nd:YAG laser can be used for small adjustments on more resistant vessels. Furthermore, pulsed light reduces pigmentation and obtains an overall rejuvenating effect of the skin.
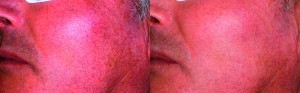
Figure 2 Phototype III, 60-year-old man with couperose on cheeks, nose and chin, as well as large telangiectasia (left). The Nd:YAG laser was used during the first session with 85 J, 15 ms, the 2.5 mm handpiece and a Peltier cooler. The second session took place 1 month later with the FT pulsed light system, with only one application with a 500 nm filter, 15 J, 8 ms (right)



